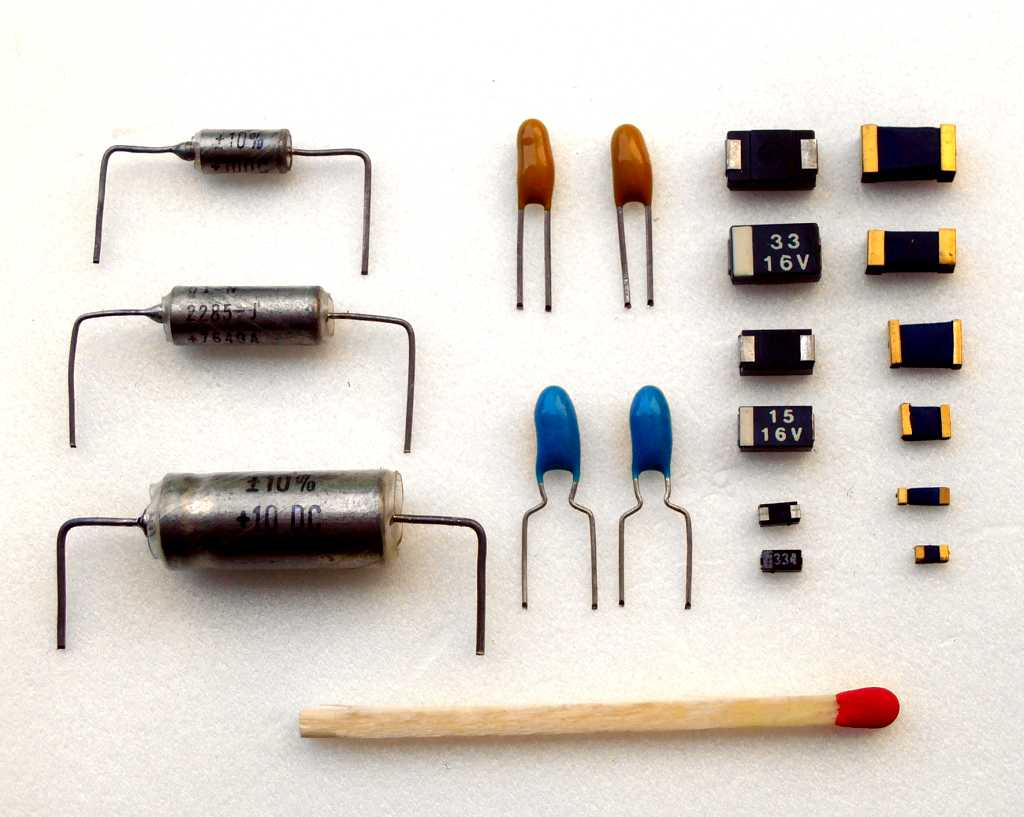
Tantalum capacitors are an essential component in electronic devices, from space technology and medical equipment to laptops and smartphones.
These capacitors have unique properties that make them suitable for a wide array of applications. They are compact, have high capacitance values, and offer low leakage current, making them a popular choice for designers looking to maximize performance while minimizing size.
But despite their popularity, many people are still unfamiliar with the ins and outs of tantalum capacitors.
In this article, we’ll examine everything you need to know about tantalum capacitors. We’ll explore their properties, the types available, their applications, and the pros and cons of using them in your designs.
Whether you’re a seasoned electronics professional or just starting in the field, this article will give you a solid foundation of knowledge on tantalum capacitors.
What is Tantalum Capacitor?

Tantalum capacitors are electronic components used to store and regulate electrical energy.
They are a type of electrolytic capacitor, which means they use an electrolyte solution to create a conductive path between two electrodes. They comprise a tantalum metal oxide anode, a Ta2O5 oxide dielectric layer, and a cathode (MnO2 or a solid polymer).
Tantalum capacitors use tantalum metal because it is highly conductive and has excellent chemical stability.
Tantalum capacitors are polarized and known for their high capacitance values, which means they can store a large amount of electrical charge relative to their size.
They are also known for their low leakage current, which makes them ideal for use in circuits that require stable and reliable performance.
Additionally, tantalum capacitors are often used in applications requiring high durability and reliability, such as in aerospace and medical devices.
Tantalum capacitors are available in a range of different styles and configurations, including surface-mount and through-hole varieties.
They are widely used in a variety of electronic devices, including smartphones, computers, audio equipment, and many others.
Tantalum capacitors typically have an operating temperature range from -55°C to +125°C.
Different Types of Tantalum Electrolytic Capacitors
There are several different types of tantalum capacitors, each with unique characteristics and applications. The main types include:
- Solid tantalum capacitor:
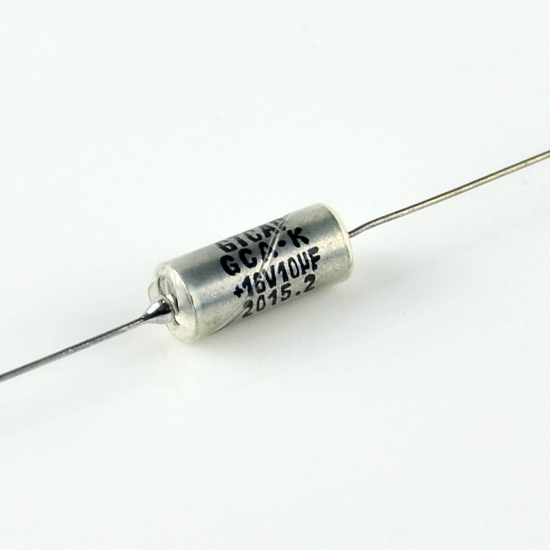
Solid Tantalum electrolytic capacitors are the most common type of tantalum capacitors. They consist of a tantalum metal anode covered with a thin layer of tantalum oxide dielectric and a cathode made of conductive material.
These capacitors use a solid form of tantalum rather than a liquid electrolyte, resulting in a more reliable and higher temperature-tolerance capacitor.
Solid tantalum capacitors are available in both surface-mount and through-hole packages and offer high capacitance values and low ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance).
- Tantalum polymer capacitors:
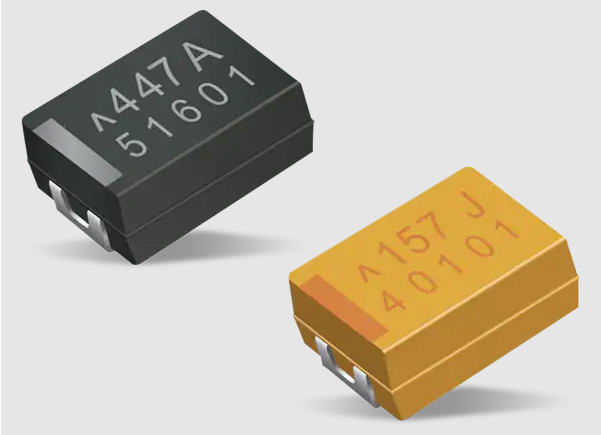
These capacitors use a conductive polymer as the electrolyte instead of a liquid electrolyte.
They offer lower ESR and better stability than solid tantalum capacitors. They are smaller and lighter than the traditional wet slug tantalum capacitors, making them ideal for applications requiring high-temperature and high-frequency filtering.
- Tantalum wet electrolyte capacitors:
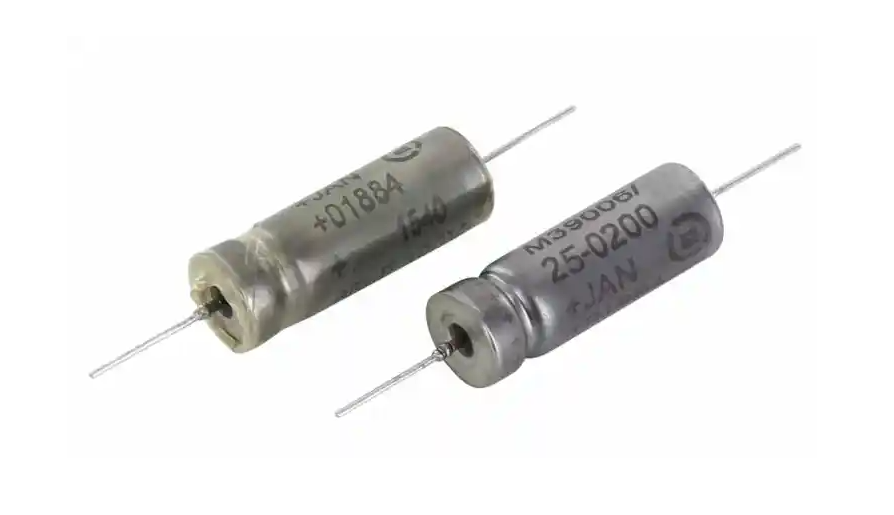

These capacitors use a liquid electrolyte instead of a solid electrolyte. They offer high capacitance values and low ESR but have a higher risk of failure due to leakage and drying out.
Wet tantalum capacitors also have a greater ability to handle surge current and a higher breakdown voltage (BDV) near their dielectric formation voltage when compared to solid tantalum technologies like MnO2 or polymer electrolyte.
As a result, these capacitors require less voltage de-rating.
Moreover, within the same temperature range, wet tantalum capacitors exhibit a higher energy density than both solid tantalum and wet aluminum electrolytic capacitors. They also have a self-healing property which gives them a higher CV value per volume unit.
Wet tantalum capacitors have the lowest leakage current among the other electrolytic capacitors and can operate at voltages over 100 V up to 630 V.
- Tantalum-niobium capacitors:
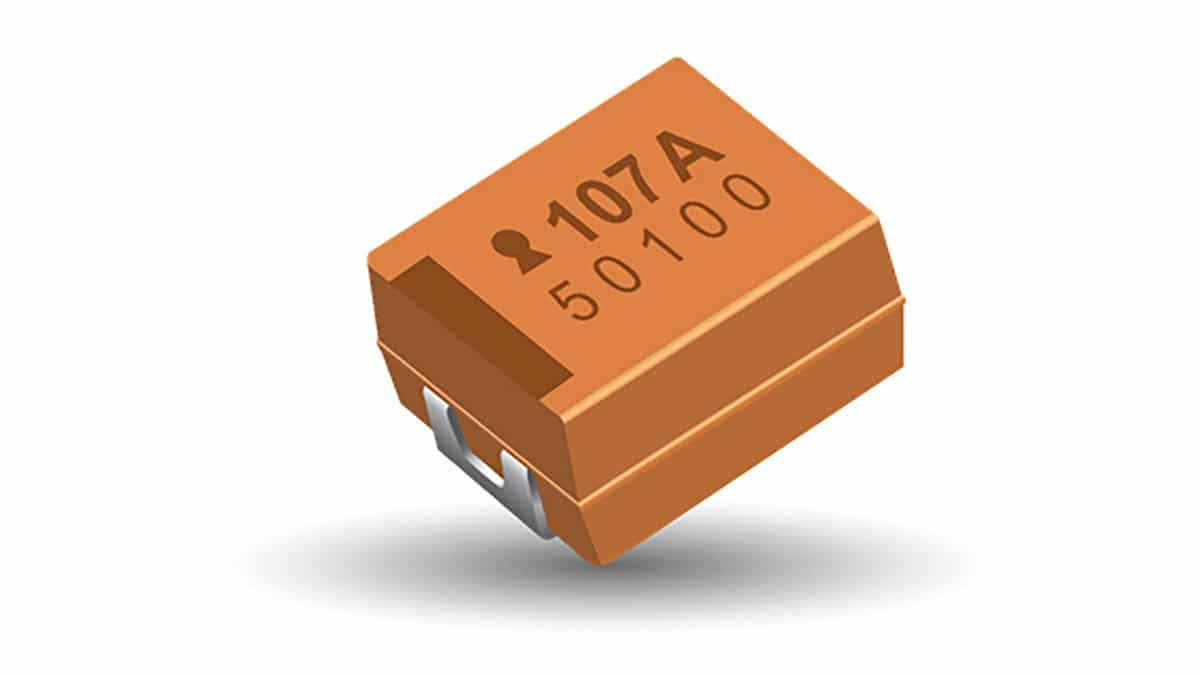
These capacitors use a combination of tantalum and niobium to create a higher capacitance per unit volume. They offer high capacitance values and low ESR, making them ideal for use in high-performance circuits.
- Hermetic tantalum capacitors:
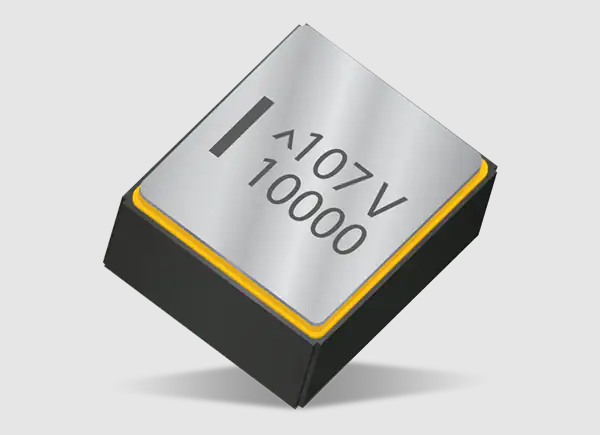

These capacitors are designed to be sealed in a hermetic package, which protects against moisture, humidity, and other environmental factors. They are commonly used in aerospace, military, and medical applications where reliability and durability are critical.
Note: Each type of tantalum capacitor has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which type to use depends on the specific application and requirements of the circuit.
Different Styles of Tantalum Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors are available in several different styles to suit various applications. Some of the most common styles include:
- Axial lead tantalum capacitors
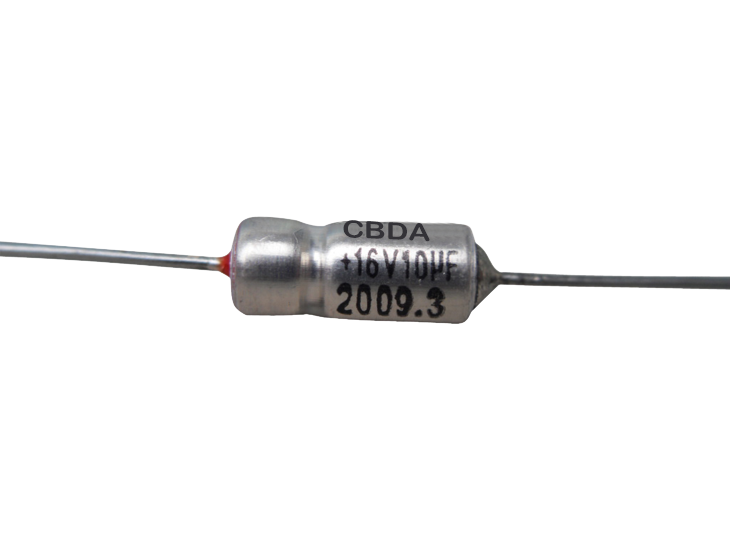

Axial lead tantalum capacitors are cylindrical, with two leads extending from each end. They are often used in circuits where a large amount of capacitance is required, but space is limited.
Axial lead tantalum capacitors are suitable for applications where a high ripple current, high level of reliability, high operating temperatures, or high vibration load is required, such as in aerospace and military equipment.
- Radial lead tantalum capacitors
Radial lead tantalum capacitors

are similar to axial lead tantalum capacitors but with leads extending from the bottom of the body.
They are typically used in applications where a high capacitance level is required, such as in power supplies and audio equipment. They are also quite valuable for space constraints applications.
- Chip tantalum capacitors (SMD Style)

Chip tantalum capacitors, also called Surface Mount Devices (SMD), are much smaller than axial and radial lead tantalum capacitors.
They are designed for use in surface mount technology (SMT) applications, where the components are mounted directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board.
SMD-style capacitors are available in various sizes and are commonly used in consumer electronics, such as smartphones and tablets.
These tantalum chip capacitors are also used in other applications where space is limited, and reliability is crucial, such as in medical equipment.
- Molded Tantalum Capacitors:
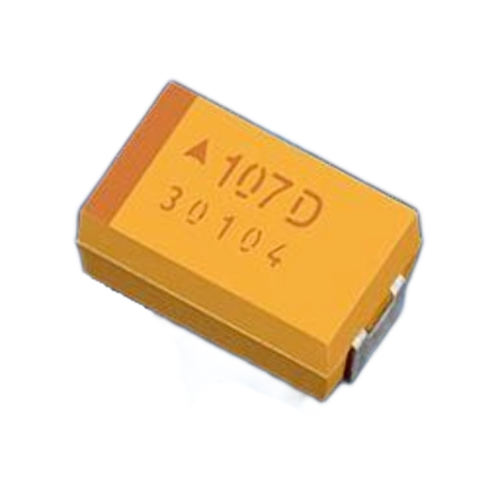

These are tantalum capacitors that are encapsulated in a molded plastic case, making them more durable and resistant to mechanical stress. They are commonly used in industrial and automotive applications.
Note: When choosing a tantalum capacitor style, it is important to ponder upon the specific application requirements.
For example, axial and radial lead tantalum capacitors are ideal for high-reliability applications, while chip and SMD tantalum capacitors are more suitable for small and portable devices.
It is also essential to consider factors such as capacitance, voltage rating, and operating temperature range when selecting a tantalum capacitor for a particular application.
Difference between Molded Tantalum Capacitors and SMD Tantalum Capacitors
The main difference between Molded Tantalum Capacitors and SMD Tantalum Capacitors is their packaging and construction.
Molded Tantalum Capacitors are enclosed in a molded plastic case, providing mechanical protection and durability.
The case is designed to prevent damage to the capacitor from vibration, shock, or thermal stress and to minimize the risk of short circuits due to contact with other components or the circuit board.
Molded tantalum capacitors are generally larger than SMD tantalum capacitors, making them more suitable for applications where space is not a constraint.
On the other hand, SMD Tantalum Capacitors (tantalum electrolytic chip capacitors) are surface-mount devices that can be directly mounted on a printed circuit board without any leads.
They are much smaller than molded tantalum capacitors and are commonly used in modern electronics where space is at a premium.
SMD tantalum capacitors are usually rectangular or square, with their capacitance and voltage ratings printed on the top.
Benefits of Using Tantalum Capacitors
- High capacitance values
Tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance values relative to their size, which means they can store a lot of charge in a small package. It makes them ideal for use in small electronic devices like smartphones and wearables.
- Low leakage current
Tantalum capacitors have a low leakage current, so they can store and regulate electrical energy without wasting power. This makes them suitable for battery-powered devices and helps extend the device’s battery life.
- Stable performance over a wide temperature range
Tantalum capacitors offer stable performance over time and at a wide operating temperature range, from -55°C to +125°C, which makes them ideal for use in harsh environments.
- Long lifespan with excellent reliability
Tantalum capacitors have a long lifespan, which means they can be used for a long time without needing to be replaced.
They are highly reliable and can withstand a wide range of environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity fluctuations.
This makes them suitable for harsh environments like aerospace and medical applications.
- Small size and low profile
Tantalum capacitors are low in profile and small, making them suitable for compact electronic devices.
- Highly Versatility:
Tantalum capacitors are available in various types and configurations, making them suitable for use in a wide array of electronic devices and applications. They can be found in everything from smartphones and laptops to industrial control systems and medical equipment.
- Low Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR):
Tantalum capacitors have a low ESR, which means they can handle high-frequency signals without losing energy and provide high-quality filtering in electronic circuits.
This is important for maintaining the performance and stability of electronic devices.
Selecting the Right Tantalum Capacitor for Your Application
When choosing a tantalum capacitor for your application, you should consider the following factors:
- Capacitance and voltage rating
Capacitance and voltage rating are crucial factors when selecting a tantalum capacitor for your application.
Capacitance refers to the amount of charge a capacitor can store, while voltage rating refers to the maximum voltage that the capacitor can withstand.
It’s essential to choose a tantalum capacitor with a capacitance value that meets the requirements of your application and a voltage rating sufficient to handle the maximum voltage in your circuit.
- ESR and ripple current
ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) and ripple current are also important factors to consider.
ESR is the resistance of the capacitor’s internal components.
Whereas the ripple current is the alternating current that passes through the capacitor. This is the maximum AC current that can be applied to the capacitor without causing excessive heating.
Choosing a tantalum capacitor with a low ESR and high ripple current capability is crucial to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
- Temperature and frequency range
Temperature and frequency range are other essential considerations when selecting a tantalum capacitor.
Tantalum capacitors typically have a wide operating temperature range (usually between -55°C to +125°C), and it’s crucial to choose one suitable for your application’s temperature range.
Similarly, the frequency range of your application must be considered, as it can affect the capacitor’s performance.
- Size and package type
Size and package type are also important factors to consider.
Tantalum capacitors come in various sizes and package types, and choosing one that fits your application’s physical requirements is essential.
It’s also important to consider the capacitor’s placement on your board and whether it can be easily accessed or replaced.
- Cost
Consider the cost of the capacitor. Tantalum capacitors are generally more expensive than other types of capacitors, so make sure that the price is justified for your application.
- Other specifications to consider
When selecting a tantalum capacitor, other specifications include its tolerance, leakage current, and reliability.
Tolerance refers to the degree of accuracy in the capacitor’s capacitance value, while DC Leakage is the amount of current that leaks through the capacitor when subjected to a DC voltage.
Choose a capacitor with a low DC leakage for applications where it is essential to minimize power consumption.
It’s also important to choose a tantalum capacitor with a high level of reliability to ensure it will perform consistently over time.
Common Uses of Tantalum Capacitors
- Power supplies and voltage regulators
Tantalum capacitors are often used in power supply and voltage regulation circuits due to their high capacitance and low ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance).
- Audio and video equipment
Tantalum capacitors are used in audio and video equipment to filter out unwanted noise and improve signal quality. They are also used in audio amplifiers and loudspeakers to improve performance.
- Computers and telecommunications
Due to their high stability and reliability, they are used in computer and telecommunication circuits, such as memory modules and motherboard circuits.
- Medical Devices and Aerospace Applications
They are used in medical devices, such as pacemakers and hearing aids, due to their small size and high reliability.
Tantalum capacitors are also used in aerospace and defense applications, such as radar systems and satellite communication systems, due to their high reliability and ability to withstand harsh environments and extreme temperatures.
Other examples and their specific uses
- LED lighting: Tantalum capacitors are used in LED lighting circuits to improve power factors and reduce harmonic distortion.
- Automotive electronics: Tantalum capacitors, such as engine control modules and anti-lock brake systems, are used in automotive electronics due to their high reliability and ability to withstand extreme temperatures and vibrations.
- Decoupling: Tantalum capacitors are used to decouple sensitive components in electronic circuits, such as microprocessors and digital signal processors, to prevent noise from interfering with their operation.
- Timing: Tantalum capacitors are used in timing circuits, such as oscillators and filters, to set the timing of signals.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Tantalum Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors are a type of electrolytic capacitor that is commonly used in electronic circuits for their high capacitance and small size.
While they offer several advantages over other types of capacitors, they can also be prone to specific issues.
Here are some common issues with tantalum capacitors and their troubleshooting:
- Overheating and thermal runaway
Overheating and thermal runaway can occur in tantalum capacitors due to excessive current or voltage, inadequate cooling, or exposure to high ambient temperatures.
Overheating can lead to decreased capacitance and leakage, and in extreme cases, thermal runaway can cause the capacitor to explode.
Troubleshooting: If overheating or thermal runaway is suspected, the circuit should be immediately turned off to prevent further damage.
The capacitor should be replaced, and the circuit should be examined for the underlying cause of the issue, such as inadequate cooling or excessive current or voltage.
Precautions:
- Choose tantalum capacitors with appropriate voltage and temperature ratings.
- Ensure proper ventilation and cooling in the circuit.
- Avoid exposing the capacitor to high ambient temperatures.
- Ensure that the circuit is designed to operate within the capacitor’s specified current and voltage ratings.
- Short circuit
Tantalum capacitors can short-circuit for various reasons, such as overheating, voltage spikes, or manufacturing defects. If a short circuit occurs, the capacitor can overheat, bulge, or even explode.
Troubleshooting: If a short circuit occurs, the capacitor should be immediately removed from the circuit and replaced. It is also essential to check the circuit for any underlying issues that may have caused the short circuit.
Precautions:
- Ensure that the circuit is designed to operate within the capacitor’s specified current and voltage ratings.
- Choose tantalum capacitors with appropriate surge current ratings.
- Ensure proper installation and soldering to prevent accidental short circuits.
- Use fuses or other protection devices to prevent excessive current flow through the capacitor.
- Open circuit
An open circuit can occur in tantalum capacitors due to manufacturing defects, mechanical stress, or exposure to high temperatures.
An open circuit can cause the capacitor to fail, leading to decreased capacitance or even complete failure.
Troubleshooting: If an open circuit is suspected, the capacitor should be replaced, and the circuit should be examined for the underlying cause, such as mechanical stress or overheating.
It is also vital to use tantalum capacitors with appropriate voltage and temperature ratings and to ensure proper handling and installation of the capacitors to prevent mechanical stress.
Precautions:
- Handle the capacitors with care to avoid mechanical stress.
- Ensure proper installation and soldering to prevent mechanical stress and overheating.
- Avoid exposing the capacitor to high temperatures.
- Leakage
Tantalum capacitors can experience leakage due to aging, overheating, or overvoltage. Leakage can result in decreased capacitance and can also damage other components in the circuit.
Troubleshooting: If leakage is suspected, the capacitance of the tantalum electrolytic capacitor should be measured to check if it has decreased significantly.
If the capacitance has decreased, the capacitor should be replaced. Additionally, the circuit should be checked for any over-voltage or overheating issues that may have caused the leakage.
Precautions:
- Choose tantalum capacitors with appropriate voltage and temperature ratings.
- Avoid exposing the capacitor to high temperatures or humidity.
- Ensure proper handling and installation to prevent mechanical stress.
- Regularly monitor the leakage current of the capacitor to detect any significant changes.
- Excessive ESR and ripple current
Tantalum capacitors can experience excessive equivalent series resistance (ESR) and ripple current due to aging, exposure to high temperatures, or improper installation.
Excessive ESR and ripple current can cause the capacitor to overheat, leading to decreased capacitance or even failure.
Troubleshooting: If excessive ESR or ripple current is suspected, the capacitance and ESR of the capacitor should be measured to check for any significant changes.
If the values have changed significantly, the capacitor should be replaced, and the circuit should be examined for the underlying cause, such as exposure to high temperatures or improper installation.
It is also vital to use tantalum capacitors with appropriate ESR and ripple current ratings and to ensure proper installation and cooling in the circuit.
Precautions:
- Choose tantalum capacitors with appropriate ESR and ripple current ratings.
- Ensure proper installation and cooling in the circuit.
- Avoid exposing the capacitor to high temperatures.
- Electrical and mechanical stress
Tantalum capacitors can experience electrical and mechanical stress due to various factors such as voltage spikes, vibration, or exposure to high temperatures.
Electrical and mechanical stress can cause the capacitor to fail, leading to decreased capacitance or even complete failure.
Troubleshooting: If electrical or mechanical stress is suspected, the circuit should be examined for the underlying cause, such as voltage spikes or vibration.
The capacitor should be replaced, and it is crucial to use tantalum capacitors with appropriate voltage and temperature ratings and to ensure proper handling and installation of the capacitors to prevent mechanical stress.
Precautions:
- Ensure that the circuit is designed to operate within the capacitor’s specified voltage and temperature ratings.
- Use proper voltage regulation to prevent voltage spikes.
- Avoid exposing the capacitor to vibration or mechanical shock.
- Failure modes and diagnostic techniques
Tantalum capacitors can fail for various reasons, including short circuits, leakage, overheating, open circuits, and excessive ESR and ripple currents.
Diagnostic techniques for identifying these failure modes include capacitance and ESR measurements, visual inspection for bulging or discoloration, and X-ray inspection for internal defects.
Troubleshooting: If a failure mode is suspected, diagnostic techniques such as capacitance and ESR measurements, visual inspection, or X-ray inspection can be used to identify the cause of the issue.
The capacitor should be replaced, and the circuit should be examined for any underlying issues that may have caused the failure.
It is also vital to use tantalum capacitors with appropriate ratings and to ensure proper handling and installation of the capacitors to prevent failure.
Precautions:
- Regularly monitor the capacitance and ESR of the capacitor to detect any significant changes.
- Polarity issues:
Tantalum capacitors are polarized and must be inserted in the circuit with the correct polarity. If the polarity is reversed, the capacitor can fail or even explode.
Troubleshooting: If a tantalum capacitor has been inserted with the wrong polarity, it should be immediately removed and replaced with a new one.
It is also essential to check the circuit for any other components that may have been damaged due to the reversed polarity.
Precautions:
- Always observe the polarity markings on the capacitor.
- Use tantalum capacitors with the correct polarity for the circuit design.
- Ensure proper installation and soldering to prevent accidental reversal of the polarity.
- Voltage de-rating:
Tantalum capacitors are sensitive to voltage spikes and can be damaged if they are subjected to voltage levels higher than their rated voltage.
Troubleshooting: To avoid voltage de-rating issues, it is crucial to use tantalum capacitors with a voltage rating higher than the maximum voltage applied to them.
Additionally, circuits should be designed with appropriate voltage regulation to prevent voltage spikes.
Tantalum Capacitors Vs Ceramic Capacitors
Here are some points of comparison between Tantalum capacitors and Multi-layer ceramic capacitors (MLCC):
Tantalum Capacitors:
- Do not have a piezo-electric effect, so they do not produce any sound or hum.
- Not susceptible to DC bias, meaning the capacitance remains constant regardless of the voltage applied.
- Stable capacitance across a wide range of temperatures.
- Physically smaller than MLCC devices of the same capacitance rating.
- They are Polarized capacitors.
Multi-layer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCC):
- May have a piezo-electric effect, which can cause them to produce audible sounds or hum at certain frequencies.
- Susceptible to DC bias, meaning the capacitance varies with the voltage level applied.
- Capacitance is temperature dependent and may decrease at low and high temperatures.
- Vibration caused by AC voltage or noise may produce audible noise.
- They are Non-polarized capacitors.
Conclusion
Due to their excellent electrical properties, Tantalum Capacitors are reliable and high-performance electronic components used in various applications.
They are available in different types, such as solid tantalum capacitors, tantalum wet electrolytic capacitors, and tantalum polymer capacitors, among others.
When selecting the suitable tantalum capacitor for your project, consider factors such as capacitance, voltage, and ESR.
Tantalum capacitors, known for their high capacitance density and reliability, are seeing several developments and trends. These include miniaturization, higher capacitance and voltage ratings, low ESR for high-frequency applications, environmental friendliness, and integration with other components.
According to the report, the global tantalum capacitor market is projected to reach US$ 1,934 million in 2026, with a CAGR of 5.58%.
Researchers are exploring new materials and manufacturing processes for higher capacitance and voltage ratings. Capacitors with low ESR reduce energy loss and improve efficiency, while sustainability is also a key consideration.
Finally, integrating tantalum capacitors with other components is seen as a way to improve performance, reduce size and cost, and push the boundaries of electronic design.
Overall, tantalum capacitors are an excellent choice for electronic projects that require high reliability and performance.
Proper selection, installation, and troubleshooting techniques are necessary for optimal performance.
It is always recommended to follow manufacturer guidelines and to consult with a qualified engineer if necessary.
With their numerous benefits and advancements in technology, tantalum capacitors will remain a popular choice for electronic applications in the future.

